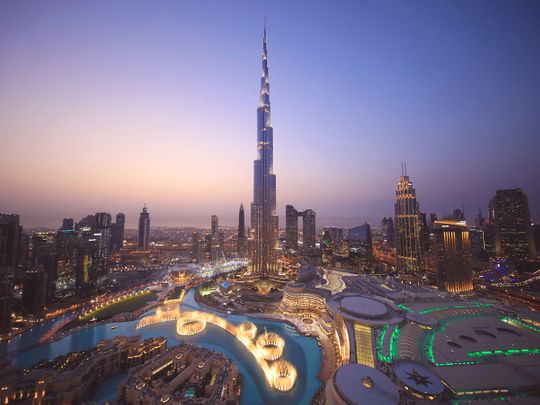

Want to know about the UAE? Well, it is natural to be curious about a country that so many people from around the world are keen to come work and live in. An ancient land, but a relatively young federation that has become iconic in how it has achieved progress and become a nation of the future.
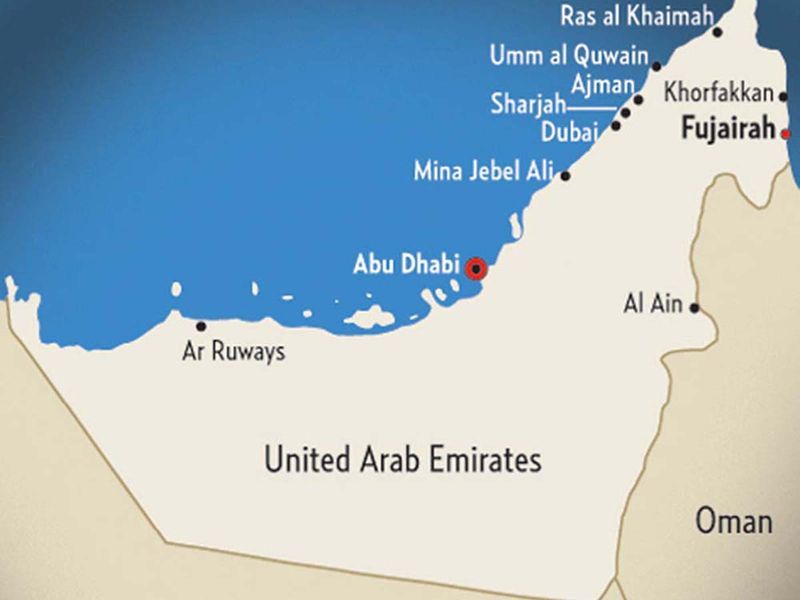
The UAE or United Arab Emirates comprises seven Emirates or states, which include the capital Abu Dhabi, Dubai, Sharjah, Ajman, Ras Al Khaimah, Fujairah and Umm Al Quwain.


When you travel through the UAE and witness its constantly changing skyline driven by vision and innovation, one cannot but help be held in its thrall. It is truly the pearl of the Arabian Gulf, exquisite in its brilliance and endurance.
History of the UAE
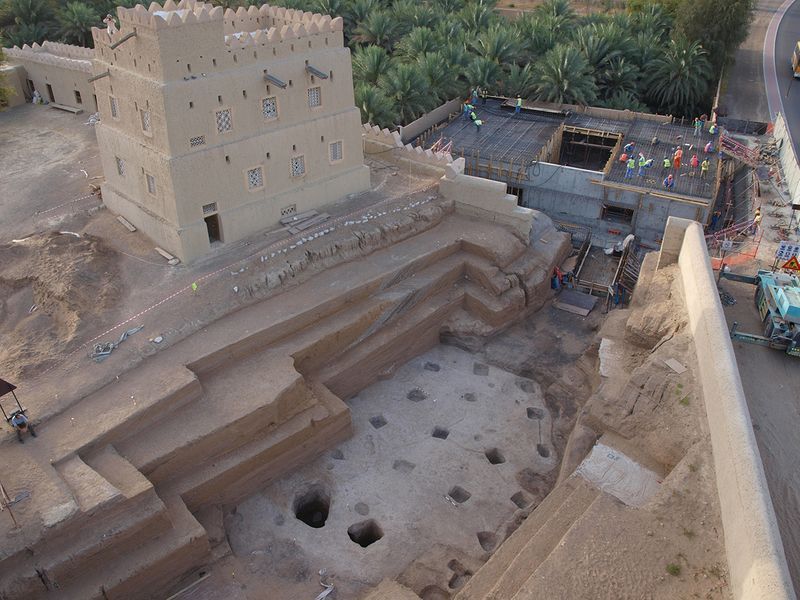

The area's history can be traced back to 6000 BC. The UAE as a federation did not exist then. The area and the surrounding region was referred to as Arabian Peninsula.
Archaeological excavations in the UAE have revealed ancient civilisations, starting with what is known as the Stone Age, the period between 6000 BC-3500 BC till the end of the Iron Age 1300 BC-300 BC.
Islamic civilisation flourished in the Arabian Peninsula and neighbouring regions during the Umayyad Caliphate from 661 to 750 AD and the Abbasid Caliphate (750 AD-1258 AD).
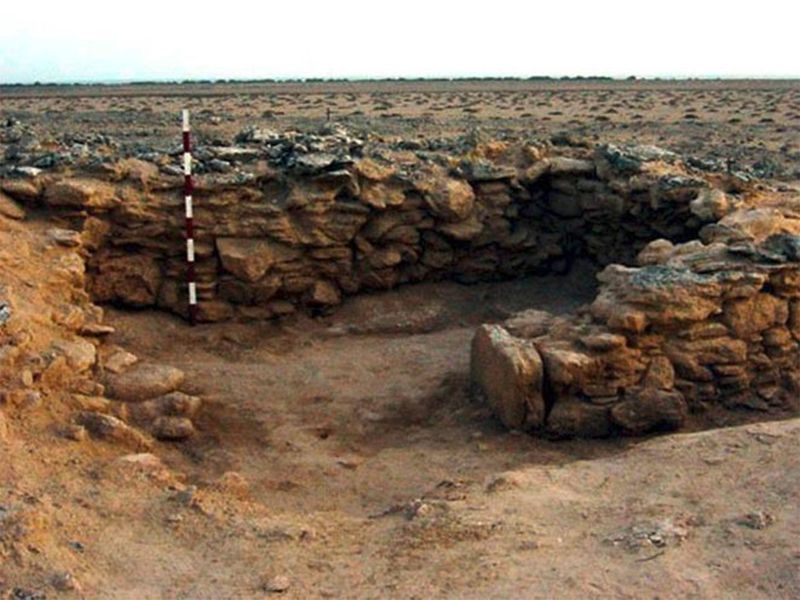

One of the oldest known Islamic landmarks in the region is the Al Badia mosque in the emirate of Fujairah, which dates back to the fifth century and is considered one of the oldest in the UAE.
Islamic power continued to dominate the Arabian Peninsula till 1492. In the same period, the interest of the European empires in the Gulf region and the sea routes leading to the commercial areas of India and Southeast Asia grew.

First the Portuguese arrived, then the Dutch, eventually followed by the British. By 1720, British business activities had grown in the Gulf region.

The British were primarily concerned with strengthening their naval power to protect trade routes to India.
Britain signed a series of agreements with the Gulf kingdoms between 1820 and 1853. According to these agreements, the leaders agreed to not enter into agreements or make contact with any power or country other than the British. In return, the British would defend the region but not interfere in internal issues. But that was a promise which did not last long because of the prospect of oil being discovered. They started getting involved in the internal affairs of the kingdoms.
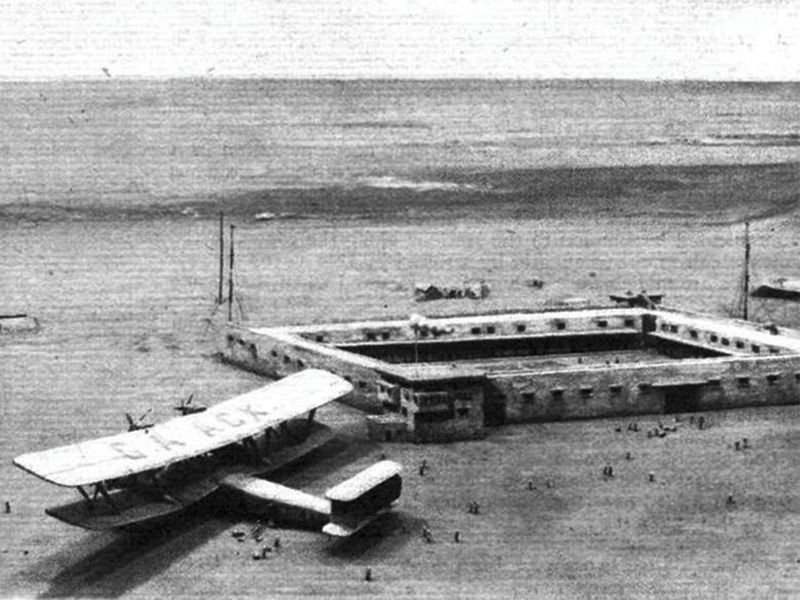

Eventually, the cost of it all became too much and the British government withdrew from the Gulf region on November 30, 1971.
Creation of the UAE Federation
The UAE was founded on December 2, 1971 and comprises seven emirates: Abu Dhabi, Dubai, Sharjah, Ajman, Umm Al Quwain, Ras Al Khaimah and Fujairah.

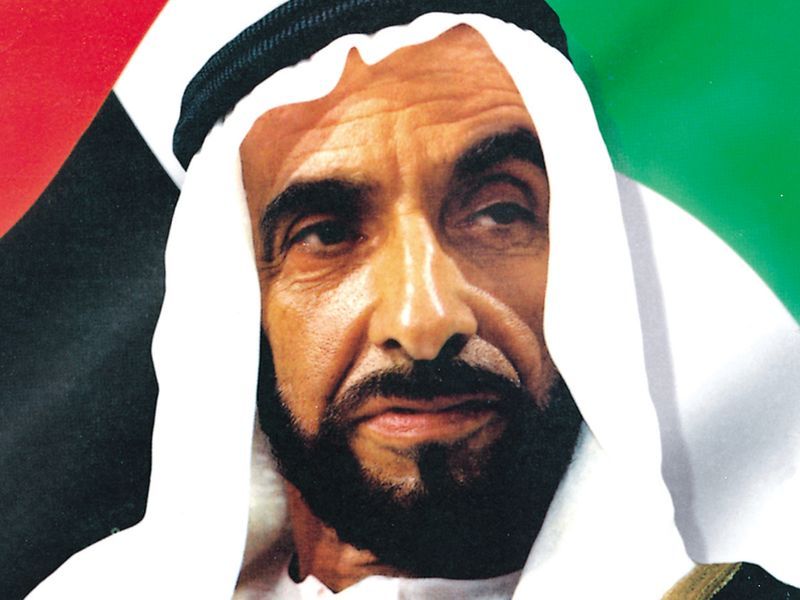
Soon after assuming power on August 6, 1966, as the Ruler of Abu Dhabi, Sheikh Zayed bin Sultan Al Nahyan underscored the importance of a united country.
Sheikh Zayed, along with Sheikh Rashid bin Saeed Al Maktoum, the then Ruler of Dubai met on February 18, 1968, at Al Samha in today’s Abu Dhabi near the south-western boundary of Dubai. This was the first momentous step in the history of the creation of the federation.
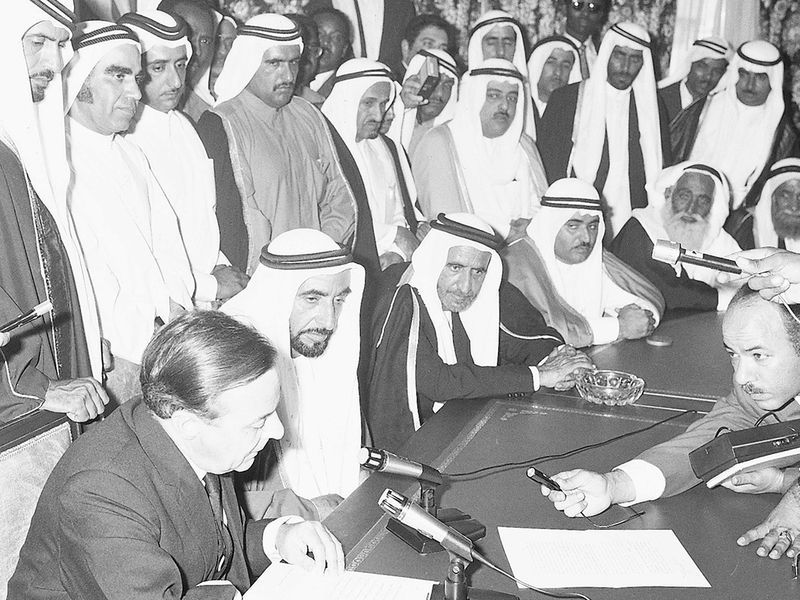

On July 18, 1971, the Rulers of six of the seven emirates that made up the Trucial States, (except Ras Al Khaimah), decided to form a union.
This meeting made the following historical declaration (as referenced on www.government.ae): “The Supreme Council felicitates the people of the United Arab Emirates, as well as the Arab people, and our friends around the world, and declares the United Arab Emirates as an independent sovereign state being a part of the Arab World.”
The Supreme Council felicitates the people of the United Arab Emirates, as well as the Arab people, and our friends around the world, and declares the United Arab Emirates as an independent sovereign state being a part of the Arab World.
Sheikh Zayed bin Sultan Al Nahyan was elected by the Rulers to be the first president of the United Arab Emirates and re-elected after a five-year term Sheikh Rashid bin Saeed Al Maktoum was elected vice president, a position he held till his death in 1990.
Ras Al Khaimah joined the federation later, on in early 1972, thus completing the Union entity, which became officially known as the United Arab Emirates.
The UAE Constitution defines five powers of the Federal State:
The Supreme Council of the Union: It is composed of the seven rulers, which is the highest institution in the country.
President and Vice President
Council of Ministers
The Federal National Council (FNC), an advisory council of 34 members, eight members each from Abu Dhabi and Dubai, six from the emirate of Sharjah and Ras Al Khaimah, and four from the remaining emirates.
Legislative or judicial power, consisting of a number of courts headed by the Federal Court.
The United Arab Emirates enjoys full independence and sovereignty. The people of all the Emirates are the same, and their citizens have the same rights.
On December 9, 1971, the UN Security Council approved UAE’s accession to the United Nations.
33 must-know facts about the UAE:
1) Abu Dhabi city is the capital of the UAE. Globally, many people are familiar with Dubai, as many travel to this emirate to work, live, shop and play - living a fabulous tax-free lifestyle

2) Sheikh Zayed bin Sultan Al Nahyan was the first President of the UAE and is known as the Father of the Nation.

3) The UAE is a constitutional federation of seven emirates.

4) The official language of the UAE is Arabic. Other widely spoken languages include: English, Bengali, Farsi, Hindi, Malayalam, Mandarin, Nepali, Russian, Sinhalese, Tagalog and Urdu.

5) Islam is the official religion in the UAE; practise of other religions is respected and allowed.

6) The UAE area is approximately 71,023.6sq km of land, including some islands in the Arabian Gulf, in addition to 27,624.9sq km of territorial water. Abu Dhabi accounts for 84 per cent of the country's total landmass. Globally, many people are more familiar with Dubai, as many travel to this emirate to work, live, shop and play - living a fabulous tax-free lifestyle

7) The UAE is 4 hours ahead of GMT.

8) The UAE has a desert climate. It is cool, with scattering of rain, in the winter and during the summer, it is hot and humid with temperatures reaching 50C.


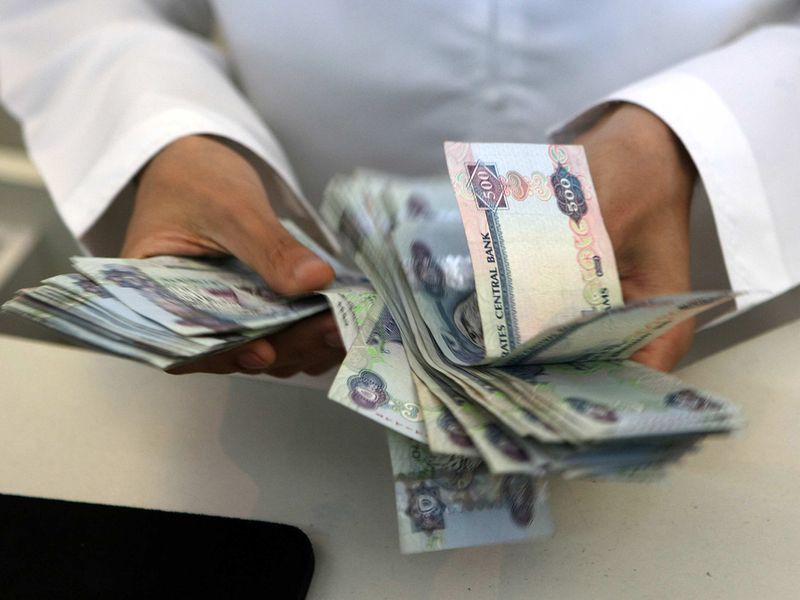
9) Dirham is the official currency and denoted as AED. Each dirham is divided into 100 fils. Coins are in the denomination of: AED 1, 50 fils and 25 fils. Notes or bills are in the denomination of AED 5, 10, 20, 50, 100, 200, 500 and 1,000. The UAE Dirham is pegged to the US dollar.

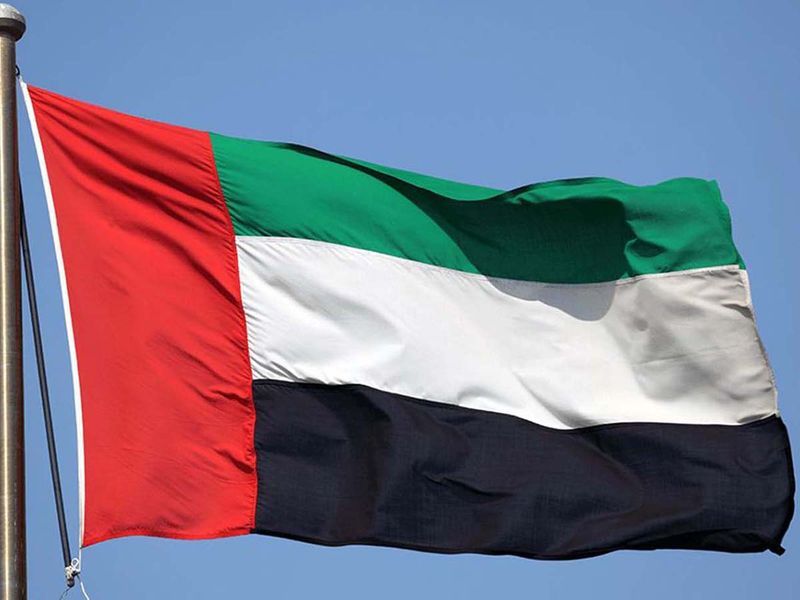
10) The flag comprises three equal horizontal lines with green at the top, white in the middle and black at the base. There is also a wider vertical red ribbon on the side of the flagpole. Green represents hope, joy, optimism and love. White represents peace and honesty. Black stands for the defeat of enemies and also strength of mind. Red represents hardiness, bravery, strength and courage.

11) The UAE's coat of arms displays the country’s flag surrounded by seven stars, representing the seven emirates. The falcon is also shown holding a parchment in its talons which reads 'United Arab Emirates' in Arabic.
12) The UAE's national anthem, Ishi Bilady was originally conceived as an instrumental in 1971. In 1986, Dr. Aref Al Sheikh was given the task to write the words to the UAE's national anthem, and the Cabinet approved the lyrics.

13) All UAE citizens are known as Emirati.

14) According to Federal Competitiveness and Statistics Authority, the UAE's total population (nationals and expatriate residents) was 9,304,277 in 2017. Males outnumber females.
15) There are more than 200 nationalities living and working in the UAE.


16) Indians form the largest expatriate community in the UAE, followed by Pakistanis, Bangladeshis, other Asians, Europeans and people from the African continent.

17) UAE nationals as of 2010 (estimate) - total: 947,997. Total non-nationals: 7,316,073
18) According to a study by Ministry of Education in 2014, the illiteracy rate in the UAE has dropped to less than 1 per cent.

19) According to Human Development report issued by the UNDP in 2016, life expectancy in the UAE is 77.1 years.

20) According to the International Monetary Fund's 2017 report, foreigners comprise 95 per cent of the UAE's workforce with the largest communities coming from South Asia.

21) As per a report issued by Federal Competitiveness and Statistics Authority in 2017, the unemployment rate was 2.5 per cent; the figure includes both nationals and expatriates.

22) The country's lowest point is at sea level and its highest point is 1,527 meters at Jebel Yibir.



23) The GDP of the UAE for 2018 in real prices amounted to approximately AED 1.6 trillion or in (US dollars: 435.70 billion) i.e an increase of 3.4%, compared to 2017.
24) The non-oil foreign trade (direct trade and free zones) of the UAE amounted to 1.527.8trillion dirhams during 2017.

25) Fiscal year is from January 1 to December 31.

26) The UAE's inflation rate was 1.97 per cent in 2017.

27) As of June 2018, the UAE's consumer price index reached 111.50.

28) The UAE does not levy income tax on individuals. However, the UAE levies 5 per cent Value Added Tax on the consumption or use of goods and services.

29) The UAE holds 4 per cent of the world's proven oil reserves and 3.5 per cent of proven gas reserves, estimated at 97.8 million barrels and 6,091 cubic metres respectively. The UAE is ranked as the seventh largest proved reserves of both oil and natural gas globally.
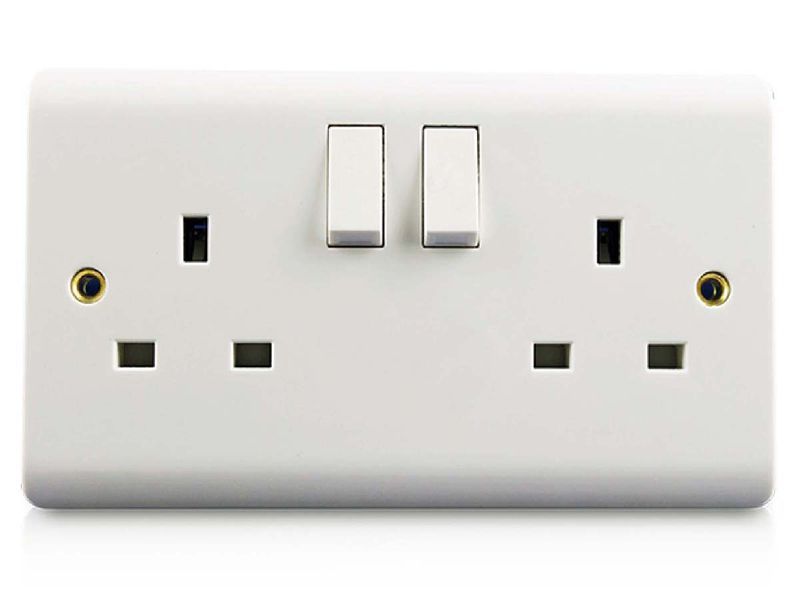
30) Domestic electric supply is 220 volts. Sockets suitable for three-pin 13 AMPs plugs of British standard design are the norm. Appliances have two-pin plugs attached.

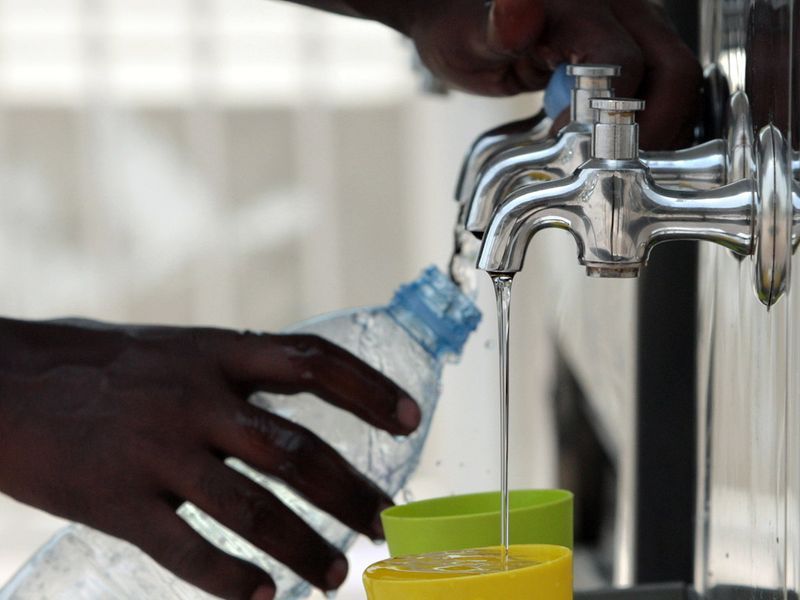
31) The water consumed in the UAE is mainly desalinated, with an average per capita consumption rate of 500 litres per day. Tap water produced by desalination is safe to drink.

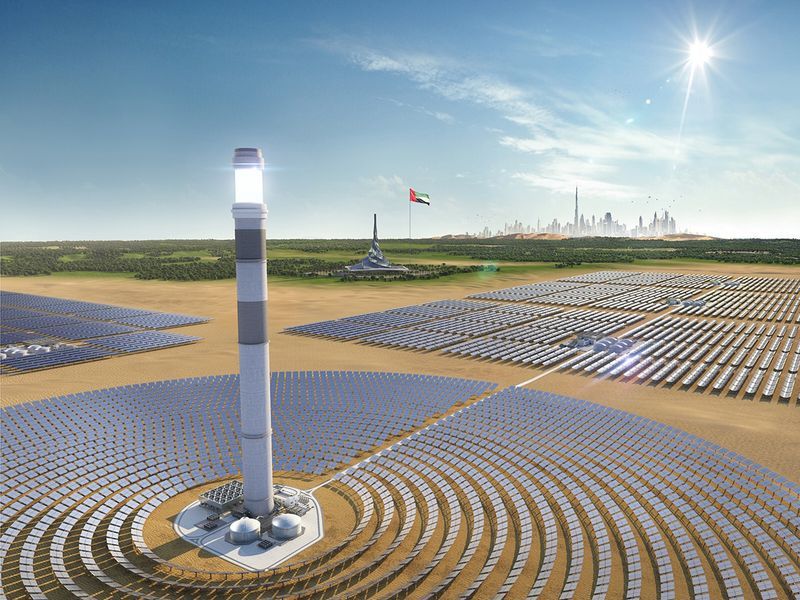
32) In 2013, the UAE was ranked third in the world in the production of concentrated solar power (CSP).

33) The UAE adopted a nuclear programme for production of electricity. Four reactors are being built at the nuclear power plant in Baraka in the Western Region of the emirate of Abu Dhabi. Upon the completion of this programme, a production capacity of up to 5600MW will be added to the national grid by 2020.




Holidays in the UAE
UAE National Day: It falls on December 2 and marks the UAE's formal nationalisation and the start of the federal unification of the emirates in 1971.

Commemoration day: It falls on December 1. It recognises the sacrifices and dedication of the sons of the nation, who have given their lives in the UAE and abroad in the field of civil, military and humanitarian service.
New Year

Eid Al Fitr

Arafat day and Eid Al Adha
Hijri New Year
Government and semi-government offices operate from Sunday to Thursday. Some private companies are closed only on Fridays while others are closed on both Fridays and Saturdays.
Telecommunications in the UAE

International dialling code: +971
The dialling codes for the emirates/cities are:
02 for the emirate of Abu Dhabi
03 for Al Ain city in the emirate of Abu Dhabi
04 for the emirate of Dubai
06 for the emirates of Sharjah, Ajman and Umm Al Quwain
07 for the emirate of Ras Al Khaimah
09 for the emirate of Fujairah and city of Khor Fakkan.
Internet domain
The top-level domain is .ae.

Official news agency, TV and radio
TV channels and radio stations are owned by government and private companies; both local and international. Content is offered mainly in Arabic and English. Other languages of broadcast include Hindi, Urdu, Malayalam, Tagalog and Farsi.
Emirates News Agency (WAM) is the official UAE news agency of the UAE Government. It publishes news in multiple languages.
Major airports in the UAE
Abu Dhabi International Airport (IATA code: AUH)

Al Ain International Airport (IATA code: AAN)
Dubai International Airport (IATA code: DXB)

Al Maktoum Airport (IATA code: DWC)
Sharjah International Airport (IATA code: SHJ)
Ras Al Khaimah International Airport (IATA code: RKT)
Fujairah International Airport (IATA code: FJR)
Roadways

Motorists drive on the right hand side of the road.
E11 - it is the longest road in the UAE. It stretches from Al Silah in the emirate of Abu Dhabi to the boundary of Ras Al Khaimah. It has various alternate names: Sheikh Maktoum Road in Abu Dhabi, Sheikh Zayed Road in Dubai and Sheikh Muhammad bin Salem Road in Ras Al Khaimah.
E311 or Sheikh Mohammed bin Zayed Road, which was known as Emirates road - the road links Dubai to the rest of the emirates.
Sheikh Khalifa highway - it links Dubai and Fujairah.
Seaports
According to the World Shipping Council, two of the world's top 50 container ports are in the UAE. Overall, 61 per cent of cargo destined for GCC states arrives via UAE seaports. Some of the major UAE ports are:
Zayed Port, Abu Dhabi
Khalifa Port, Abu Dhabi
Free Port, Abu Dhabi
Musaffah Port, Abu Dhabi
Jebel Ali, Dubai
Mina Rashid, Dubai
Sharjah Container Terminal (SCT), Sharjah
Khor Fakkan Container Terminal (KCT), Sharjah
Mina Saqr, Ras Al Khaimah
Fujairah Port










