
DUBAI: Adult stem cell therapy is dubbed as the new healing force of the 21st century, much as the internet revolutionised the past century.
Now, UAE researchers have demonstrated they're in the leading edge of this breakthrough in medicine. Abu Dhabi-based doctors have announced pioneering work in stem cell therapy to repair lung damage caused by coronavirus infection. One simple yet fascinating aspect of this new therapy: it's administered through inhalation.
It's a potential "wow" moment for immunotherapy and regenerative medicine — the Abu Dhabi team sucessfully treated 73 COVID-19 patients, who were cured of COVID-19 before hospital discharge.
Numerous vaccine trials are undeway for COVID-19, but a safe and effective jab that can be used on a massive scale on healthy patients is at least a year away.
'National achievement'
Speaking at a press conference on coronavirus updates on Saturday night, Dr. Fatima Al Kaabi, Head Hematology and ncology Department at Sheikh Khalifa Medical City in Abu Dhabi, explained the results of the stem cell therapy.
“At the Abu Dhabi Stem Cell Center, we are proud to work on developing a supportive treatment for COVID-19 patients which is undergoing clinical trials for the first time in the UAE. This is a national achievement,” Dr. Fatima Al Kaabi, who is part of the stem cell research team against COVID-19.
The announced treatment is supportive and not curative, she explained, and helps alleviate COVID-19 symptoms rather than eradicating the virus itself.
How many COVID-19 patients were treated with UAE stem cell therapy?
Treatment was administered on 73 confirmed positive COVID-19 patients, and was considered a success, after they were cured of the virus by inhaling the treatment into their lungs after it has been "nebulised into a fine mist".
The pioneering treatment is hypothesised to have its therapeutic effect by regenerating lung cells and modulating the immune response to keep it from overreacting to the COVID-19 infection and causing further damage to healthy cells.
The pioneering treatment is hypothesised to have its therapeutic effect by regenerating lung cells and modulating the immune response to keep it from overreacting to the COVID-19 infection and causing further damage to healthy cells.
73
COVID-19 patients in the UAE who have all been successfully treated -- and cured -- of the virus by inhaling the treatment into their lungs after it has been nebulised into a fine mist.Who developed the stem cell therapy in the UAE?
The treatment was developed by a team of doctors and researchers at the Abu Dhabi Stem Cell Center (ADSCC).
A patent has been granted by the UAE Ministry of Economy for the development of an innovative and promising treatment for COVID-19 infections using stem cells.

How does stem cell therapy work?
It involves extracting stem cells from the patient’s own blood and reintroducing them after "activating" them.
The treatment has successfully undergone the initial phase of clinical trials, demonstrating its safety.
IMMUNOTHERAPY OR BIOLOGICAL THERAPY: The treatment of disease by activating or suppressing the immune system. Immunotherapies designed to elicit or amplify an immune response are classified as "activation immunotherapies". immunotherapies that reduce or suppress are classified as "suppression immunotherapies".
Were there any adverse effects in the Abu Dhabi COVID-19 therapy?
None of the patients who had received the treatment reported adverse effects, according to the Abu Dhabi research team.
More importantly, there have been no interactions found with the conventional treatment protocols for COVID-19 patients.
So, cell therapy and tissue engineering are parts of the field of regenerative medicine, whose aim is production of safe and effective therapies.
Stem cells present in almost every type of tissues and represent an endogenous system of regeneration and repair. Therefore, stem cells represent great hope for the future of translational medicine.
[International Journal of Stem Cells: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC4961101/]
What is a stem cell?
A stem cell is a cell with the unique ability to develop into specialised cell types in the body. It's the basic building block of life.
In the future, they may be used to replace cells and tissues that have been damaged or lost due to disease.
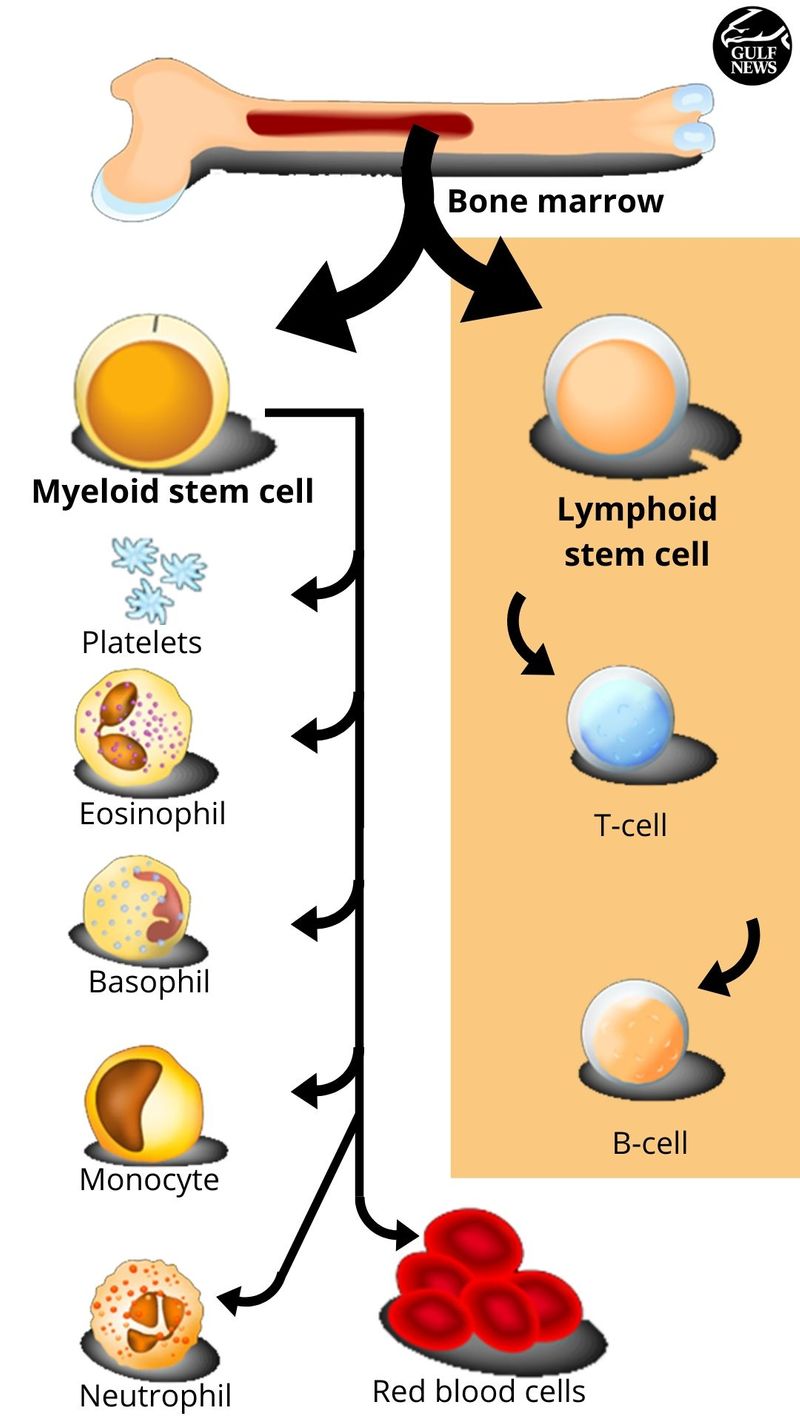
They can become cells of the blood, heart, lungs or other body parts. Stem cells also have a strong secretory function, promoting the formation of new blood vessels, cell proliferation and differentiation and inhibiting inflammatory response, experts say.
A large variety of cell types has been used for regenerative medicine, including adult cells, resident tissue specific stem cells, bone marrow stem cells, Umbilical cord blood stem cells, embryonic stem cells and the recent breakthrough discovery of induced pluripotent stem cells from mature/adult cells (iPS) (called reprogramming, induced a pluripotent state in a previously differentiated cell type).
[Source: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/19376801]
How does stem cell therapy work in general?
Stem cells can self-renew or multiply while maintaining the potential to develop into other types of cells.
For example, right now, your body's stem cells are working hard replacing your skin every two weeks, creating new red and white blood cells.
Does inhalation of stem cells actually work in repairing lung tissue?
Yes. At least two studies had demonstrated this.
First, in 2016, a team of Egyptian experts showed that stem cells help in lung regeneration, according to a study published in the International Journal of Stem Cells.
The airway epithelium is exposed to inhaled particles and pathogens that may lead to the development of a many infectious and inflammatory respiratory diseases. The study investigated promising stem cell therapy to treat lung and tracheal tissue damage.
The second recent study we found, published on Nature Communications on February 28, 2020, shows that an inhalation treatment of secretome and exosome exhibited therapeutic potential for lung regeneration.
These were based on two experimental models of pulmonary fibrosis (lung disease in which persistent injury results in scar tissue formation — as fibrosis thickens, the lung tissue loses the ability to facilitate gas exchange and provide cells with needed oxygen).
SARS-CoV-2 is a newly-discovered pathogen that primarily attacks the lungs (and airway epithelium). This leads to the development of an infectious and inflammatory respiratory disease, called COVID-19, partly as a result of the over-reaction of the human immune system which then leads to acute pneumonia — and can be deadly.
Secretome: The stem cell secretome produce tiny “communication vesicles” (paracrine soluble factors) that interact with surrounding (stem) cells. Healthy Mesenchymal Stem Cells do this intensively with signals that have almost exclusively “positive” effects on surrounding cells and hence change not only the local tissue environment but also the whole immune system. The properties of the secreted factors are anti-inflammatory, neuro- and angio-trophic, immune modulatory, anti-apoptotic, neuroprotective and anti-oxidatory.
[Sources: https://bit.ly/2YnEBqp; https://bit.ly/2WnyfEI]
Where was the first research on stem cell therapy against COVID-19 conducted?
In March, Chinese researchers announced they were studying the use of stem cell technology in the treatment of people critically ill with the novel coronavirus disease (COVID-19), Xinhuanet reported then.
How many patients were involved in Chinese stem cell clinical trial?
Four COVID-19 patients who received stem cell treatment while in a serious condition have been reportedly discharged from hospital following recovery. The Chinese researchers said they will expand the clinical trial of the therapy.
Has stem cell therapy been used to treat infectious diseases in the past?
Yes. Stem cell therapy has been used in the treatment of some infectious diseases and complications. For instance, it has been tried in treating H7N9 avian flu and showed good results.
According to the Ministry of Science and Technology, the Chinese Academy of Sciences has developed a new stem cell drug, CAStem, which has shown promising results in animal experiments.
The research team has applied for urgent assessment by the National Medical Products Administration. Approvals by the ethics committee, and clinical observation and evaluation are in progress.
What's next?
More trials to demonstrate the efficacy of the treatment are ongoing and are expected to be completed "in a couple of weeks".
The treatment has been given to patients along with the conventional medical intervention and will continue to be applied as an adjunct to established treatment protocols rather than as a replacement.
A UAE patent was granted for the innovative method in which the stem cells are collected, or "harvested".
The innovation represents a pay-off from numerous scientific research work being conducted in the UAE and laws enacted to attract talent from different parts of the world. It also promises to potentially turn the tide in the global effort to fight SARS-CoV-2.








