1 of 19

2 of 19

3 of 19

4 of 19

5 of 19
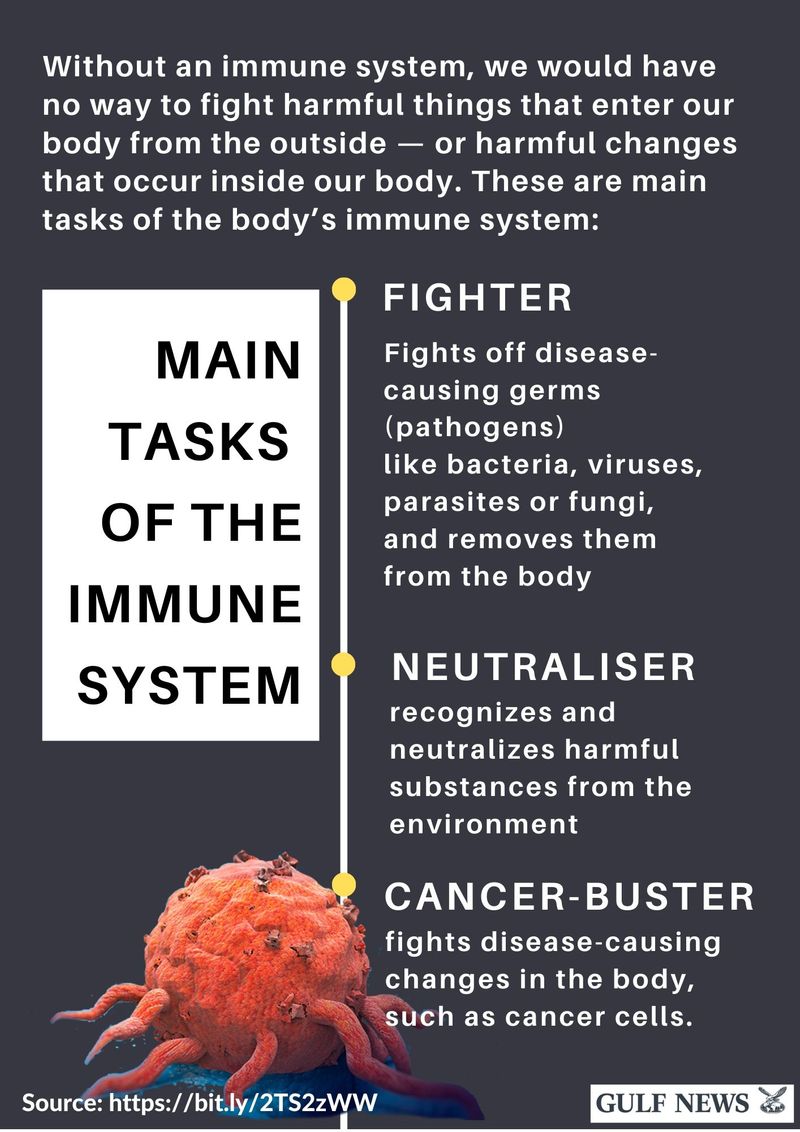
6 of 19
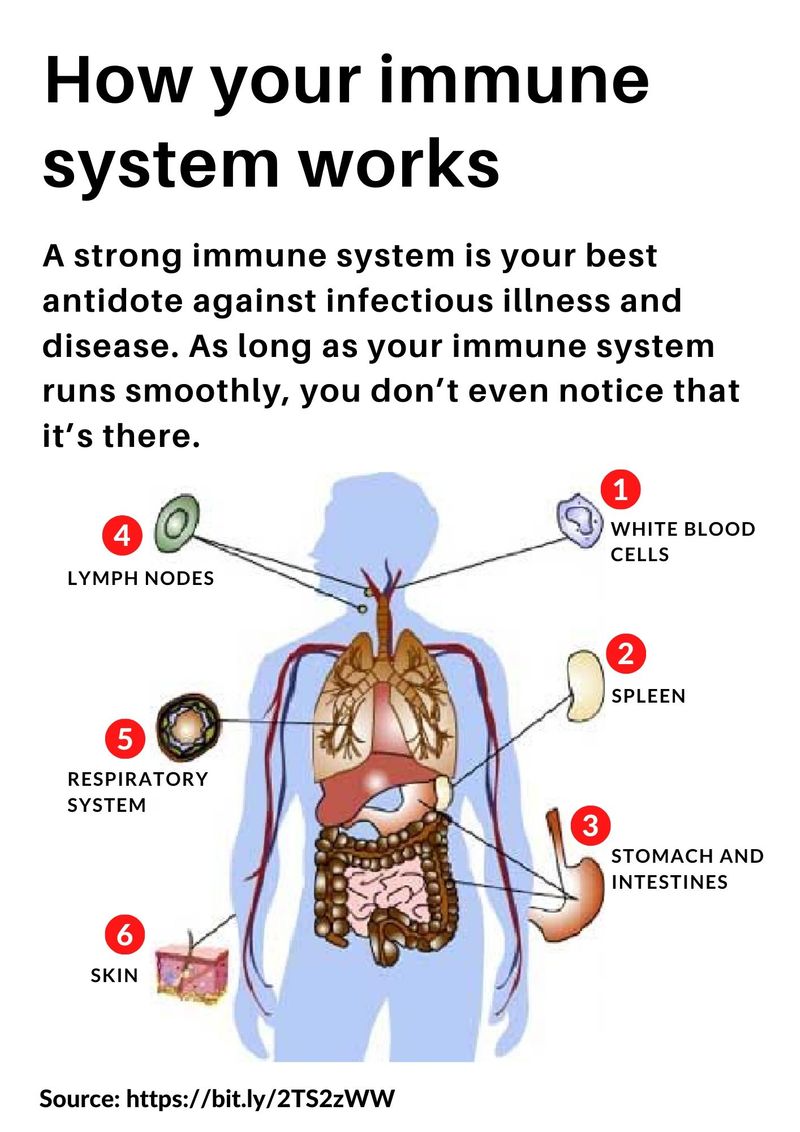
7 of 19
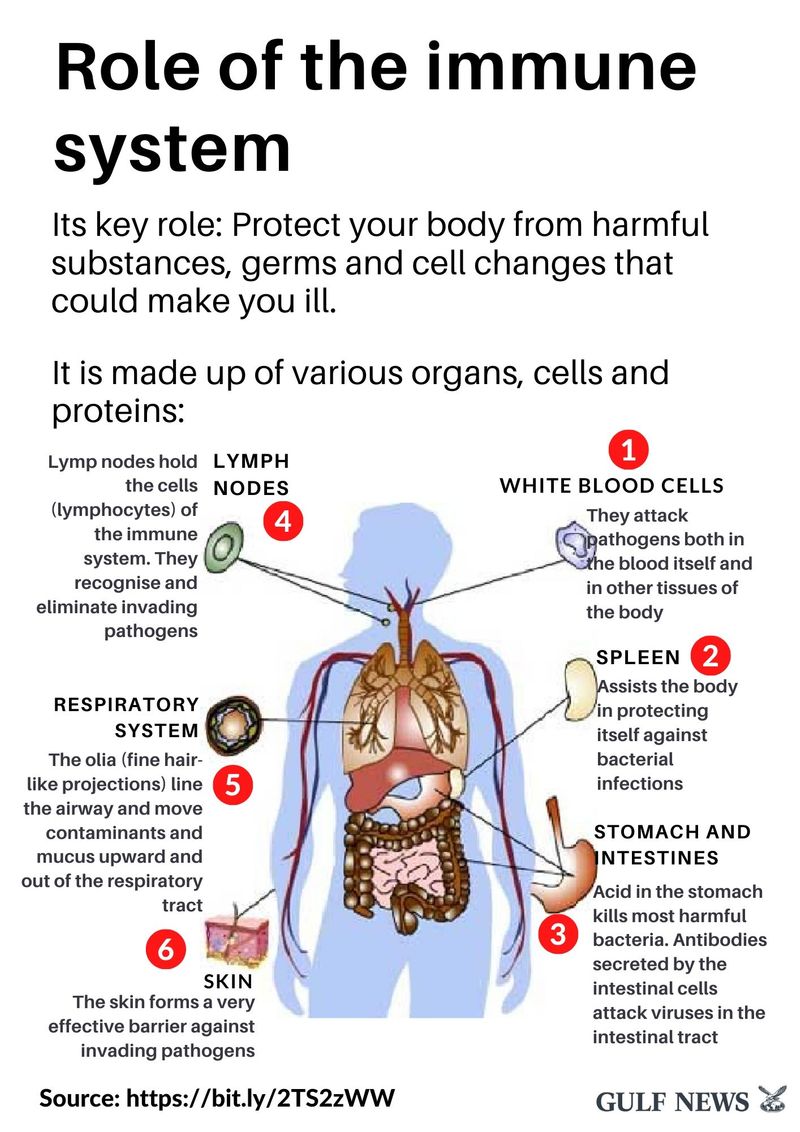
8 of 19
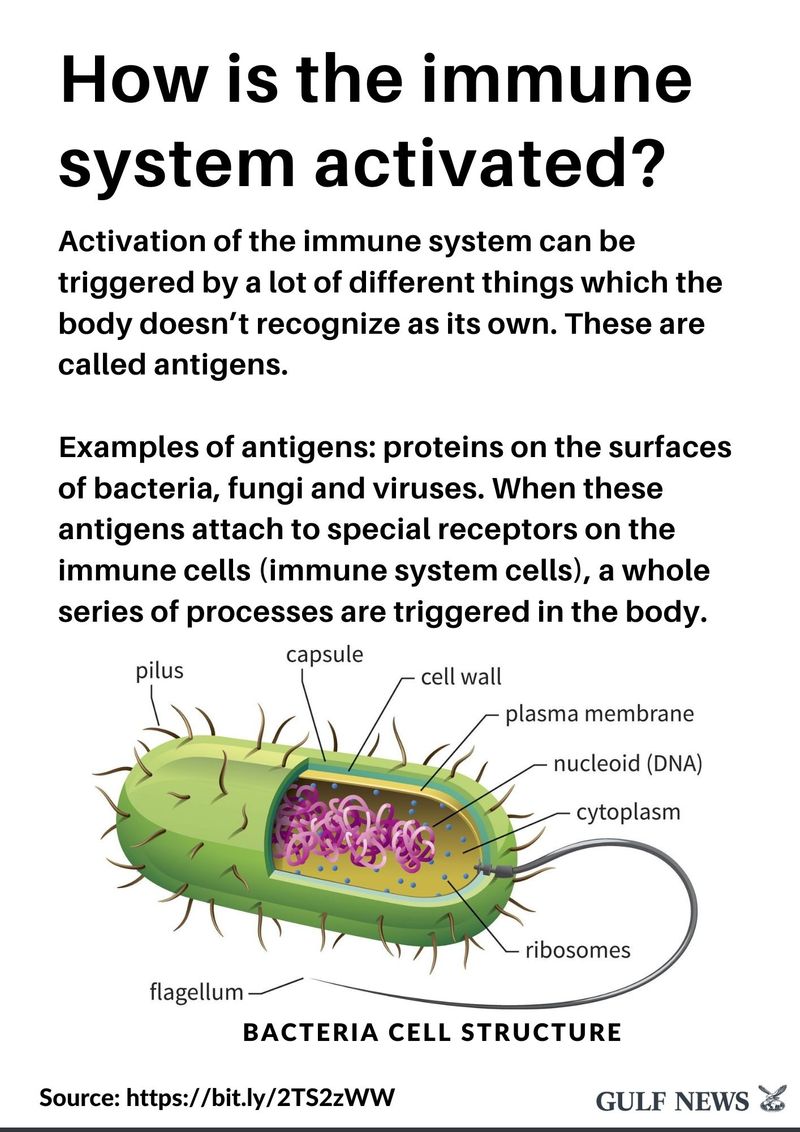
9 of 19
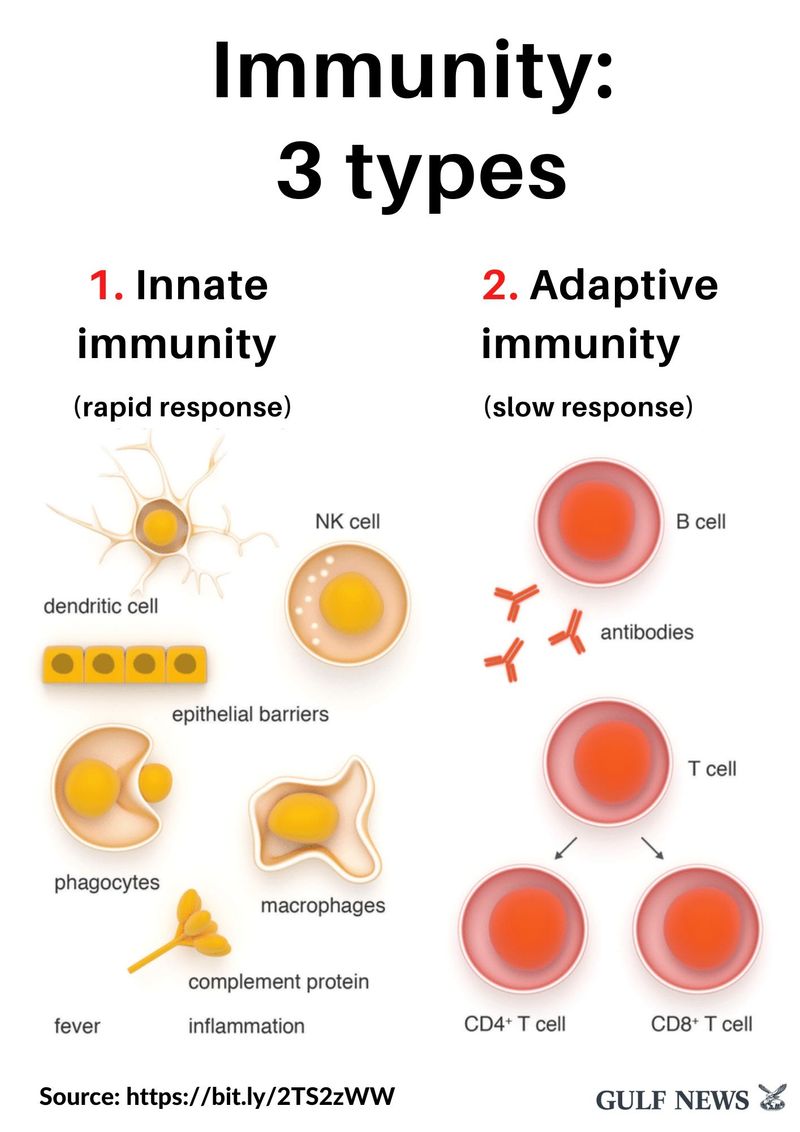
10 of 19
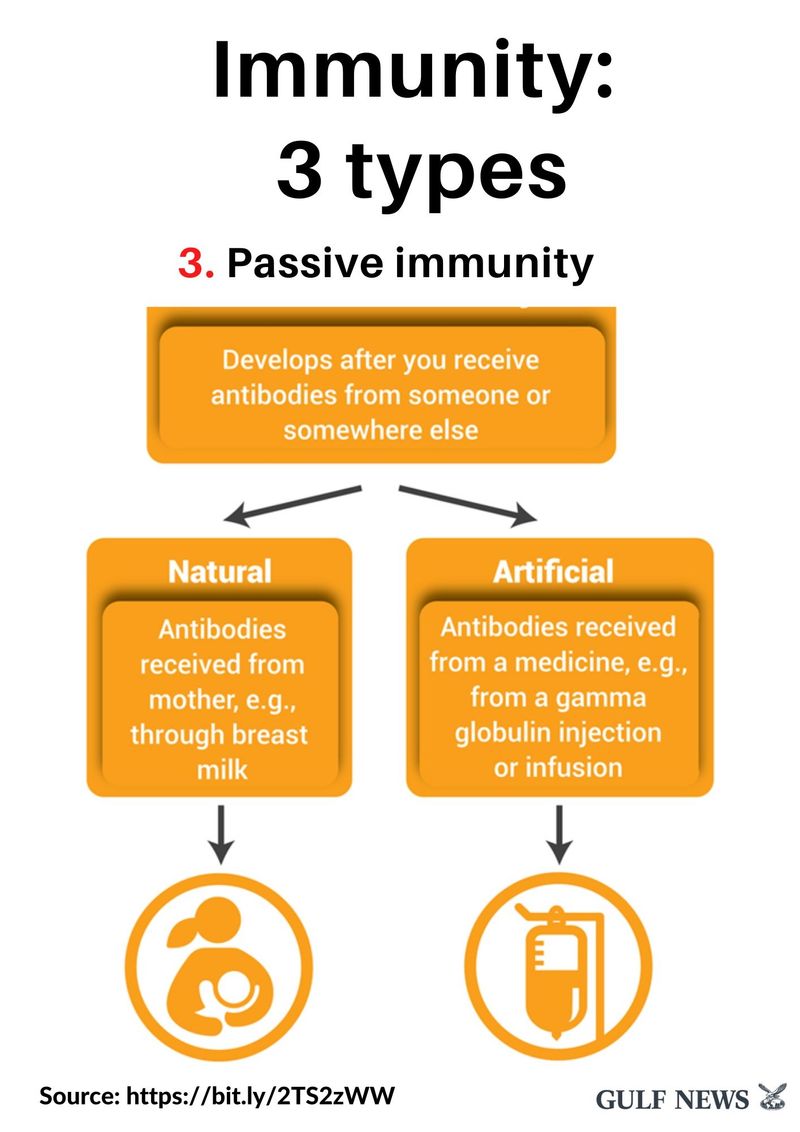
11 of 19

12 of 19

13 of 19
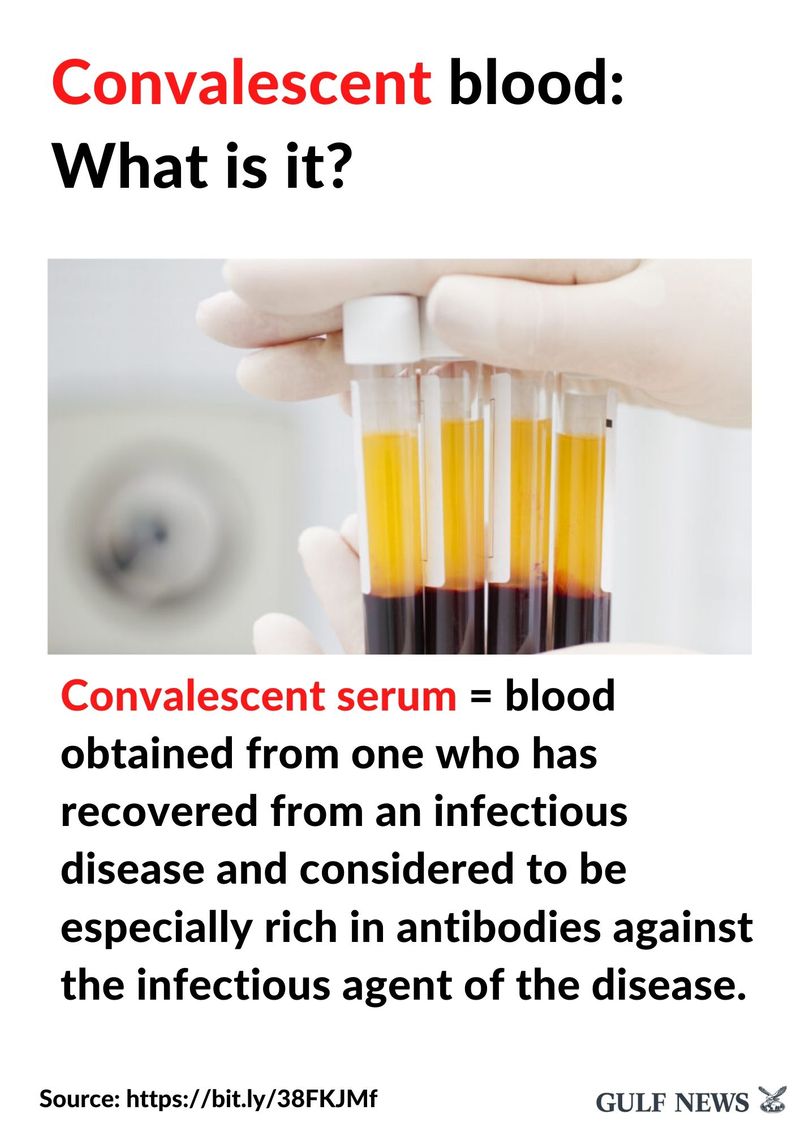
14 of 19

15 of 19

16 of 19

17 of 19

18 of 19

19 of 19









